Mineral Identification
Each layer of the Earth has a different density
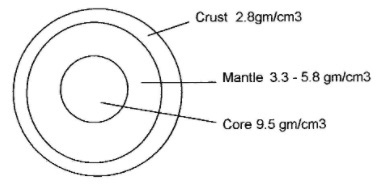
Thickness of each layer:
- Crust - 5-30 miles
- Mantle - 1800 miles
- Core - 2000 miles
Matter of the Lithosphere
Lithosphere: outer portion of the crust
- 2000 Minerals
- 88 Elements
Rock formers: 9 abundant elements in the litosphere
Common elements that make up the minerals of the crust, in decreasing abundance:
- Oxygen
- Silicon
- Aluminum
- Iron
- Calcium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Titanium
Organic: Once living; ex: coral, mollusk, shells
Inorganic: Never living
Minerals..
- are inorganic
- formed in nature
- solids
- have a definite internal atomic pattern
- have a specific chemical composition (compound)
We can observe the internal atomic pattern by use of X-ray defraction.
If the arrangement of the molecules is large enough to be recognized by the eye, we call it a Crystal.
Large crystals are uncommon because when crystals start to form they interfere with each other. Instead of growing into large recognizable crystals, the crystals grow together -- the mineral is said to be massive.
Mineralogist: a scientist who studies minerals.
Groups of Minerals
-
Silicates
Si + O -- largest group; 87% of the crust
-
Carbonates
C + O
- Ca + C + O2 => CaCO2
- Mg + C + O2 => MgCO2
- Fe + C + O2 => FeCO2
To test for a carbonate, place a drop of HCl (hydrochloric acid) on the sample. If it fizzes, it's a carbonate.
-
Oxides
O2 + some other element, e.g. Fe2O3
Tetrahedron structure: basic unit of all silicates
Silica is SiO4. The atoms are arranged with Si in the center:

Crystal faces: the flat surfaces which join at well defined angles.
The angle between crystal faces is always the same, regardless of size.
Identification of Minerals
-
Luster: the wasy that it reflects light
- Metallic: looks like a metal
- Non-metallic: does not reflect light like a metal
Non-metallic luster terms:
- Adamantine - sparkles like a diamond
- Vitreous - like a broken edge of glass
- Greasy
- Pearly
- Silky
- Waxy
- Dull - lacks luster; scatters light
- .. other terms can also be used
-
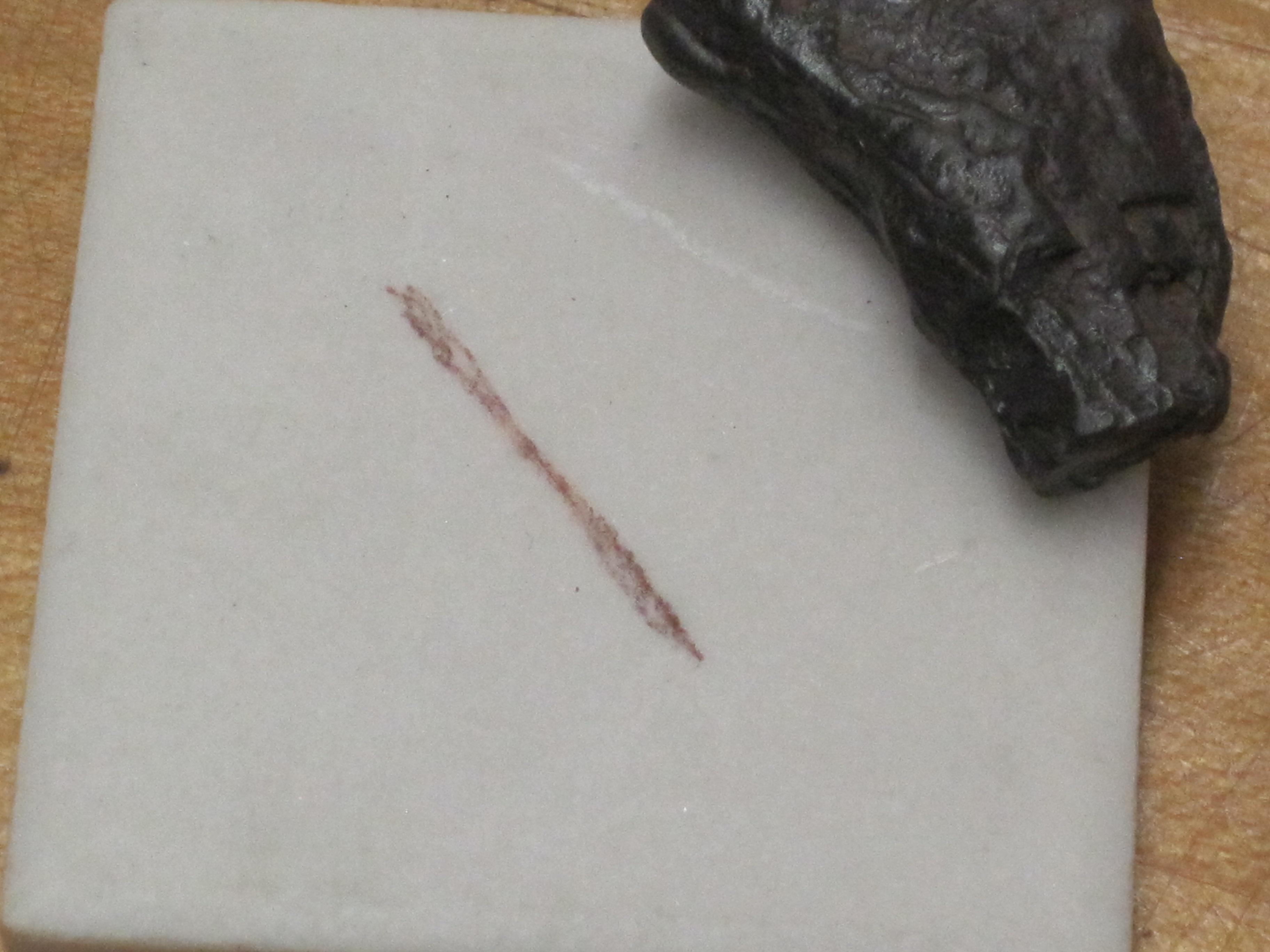
Streak: the color of the powdered mineral
Rub the mineral on a porcelain plate. The color that comes off the mineral is called the streak color.
-
Hardness: resistance to being scratched
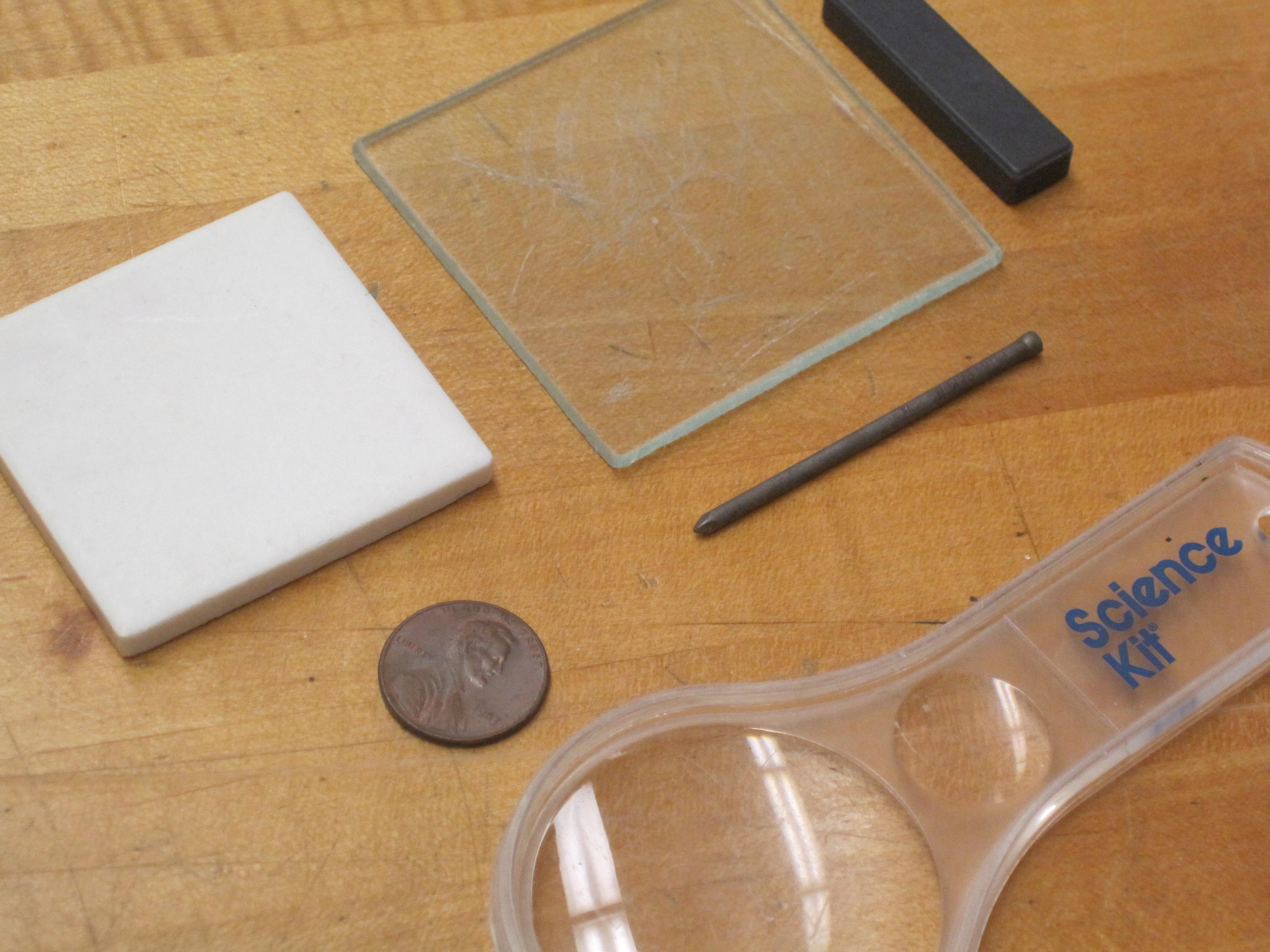
Mohs Scale of Hardness
Mohs Scale Field Test 1. Talc Soft, feels greasy 
2. Gypsum Scratched by fingernail 
3. Calcite Scratched by a penny 
4. Fluorite Easily scratched by a knife blade 
5. Apatite Scratched by a knife blade with difficulty 
6. Feldspar Scratched by glass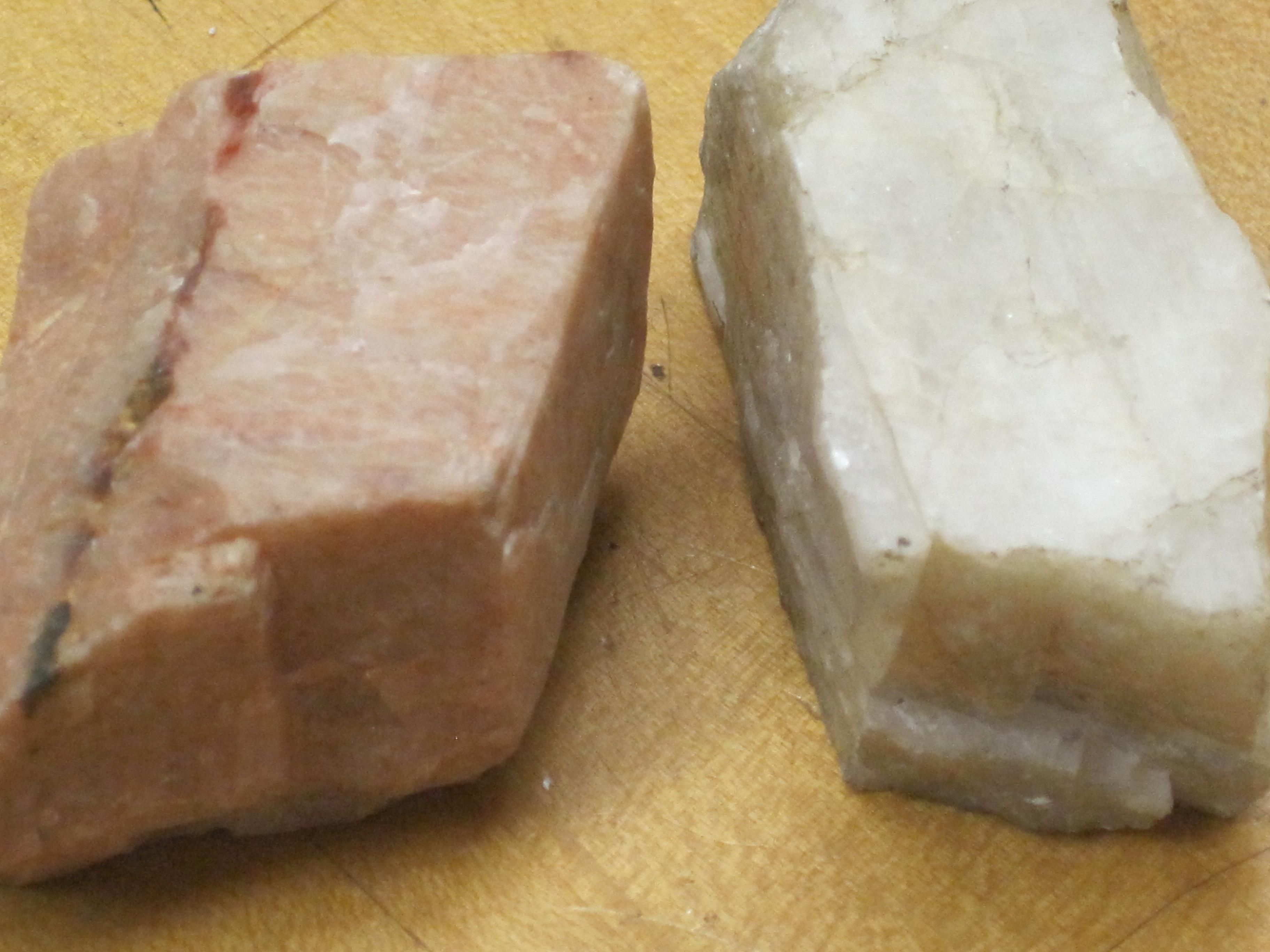 
7. Quartz Will scratch glass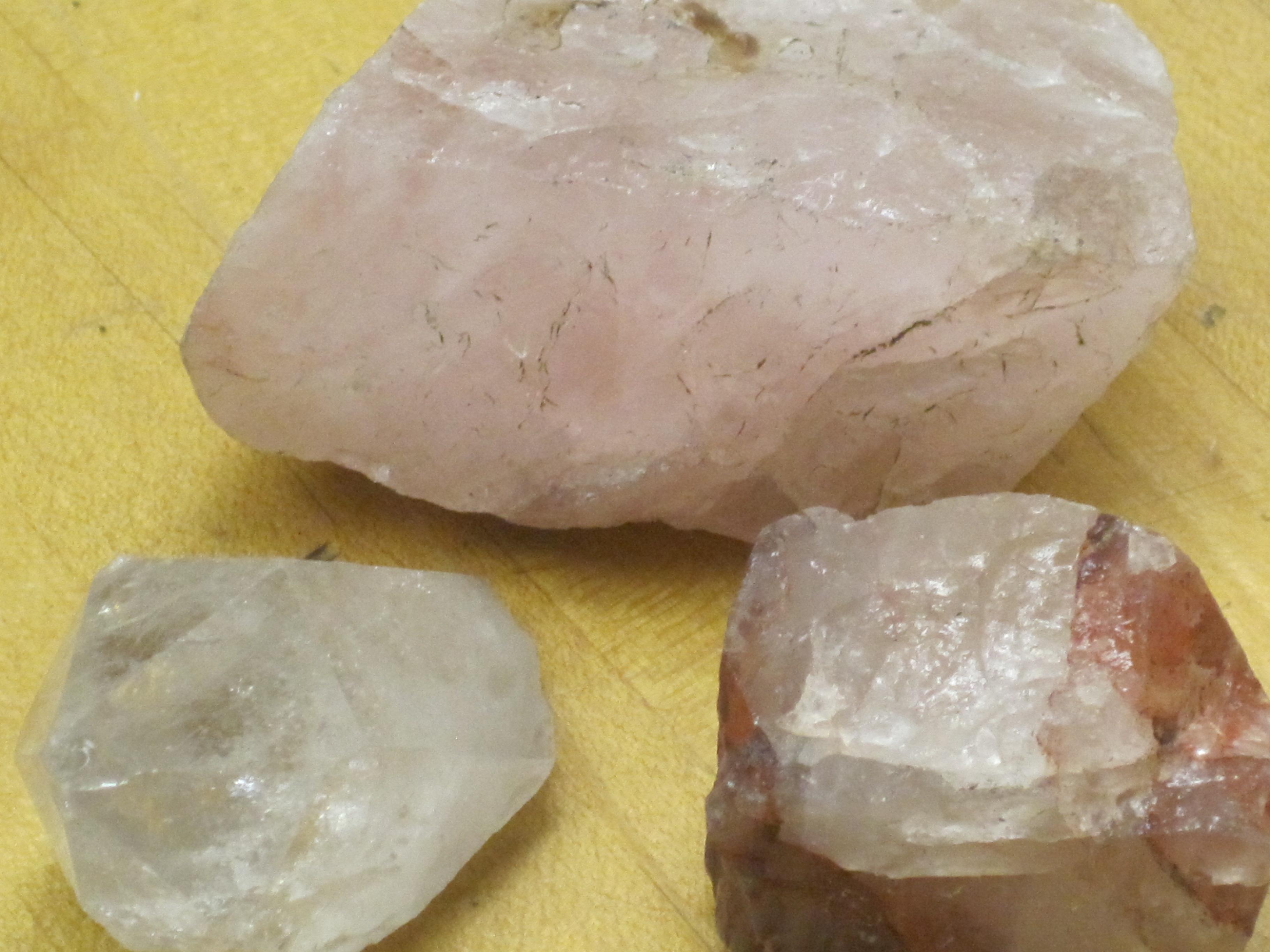 
8. Topaz Scratches quartz 
9. Corundum Scratches topaz 
10. Diamond Scratches corundum 
-
Shape: external appearance
-
Amorphous: without a definiate shape, massive

-
Crystal: definite geometric pattern; count the number of crystal faces

Some terms that can be used for minerals that have a definite shape:
- Prismatic
-
Micaceous

- Acicular
- Pisolitic
- Tabular
- Oolitic
-
Fibrous
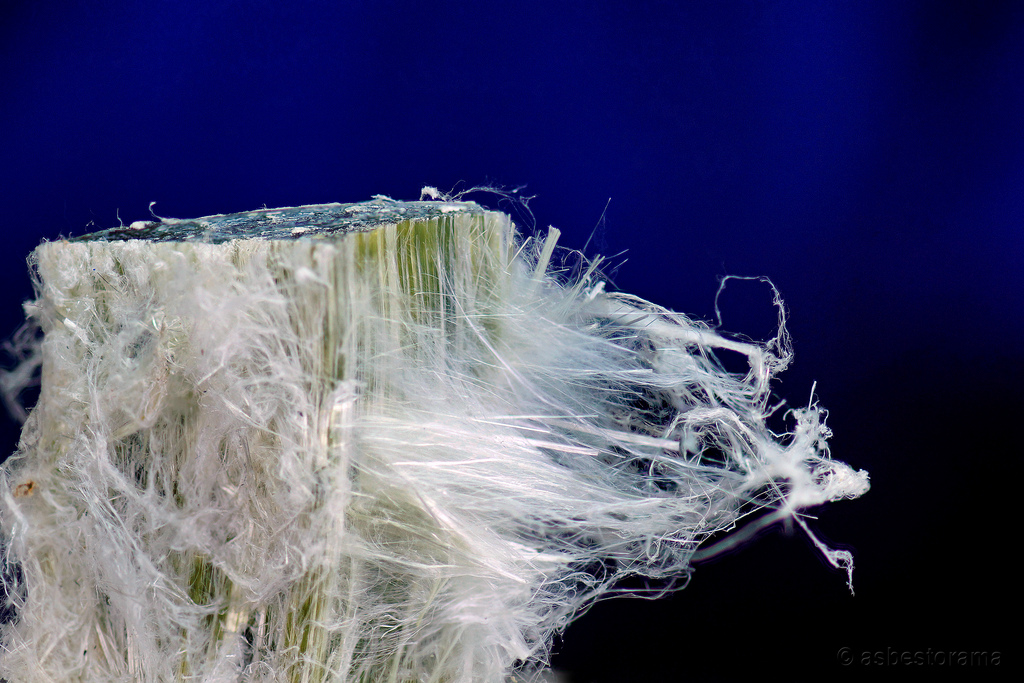

-
-
Breakage
-
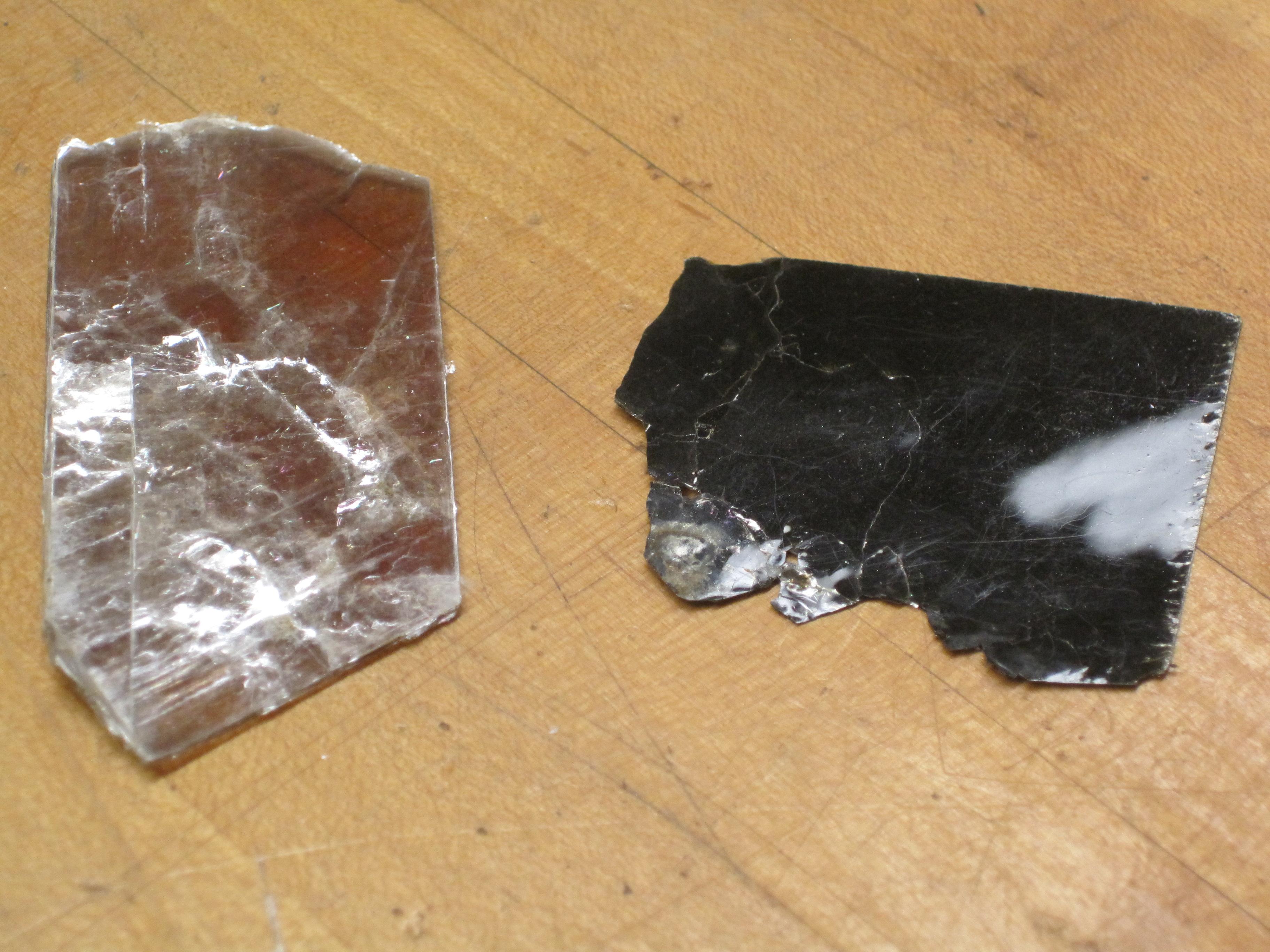
Cleavage: breaks along smooth plane, surfaces that are parallel to the opposite surface: 1-, 2-, or 3- direction cleavage.

-
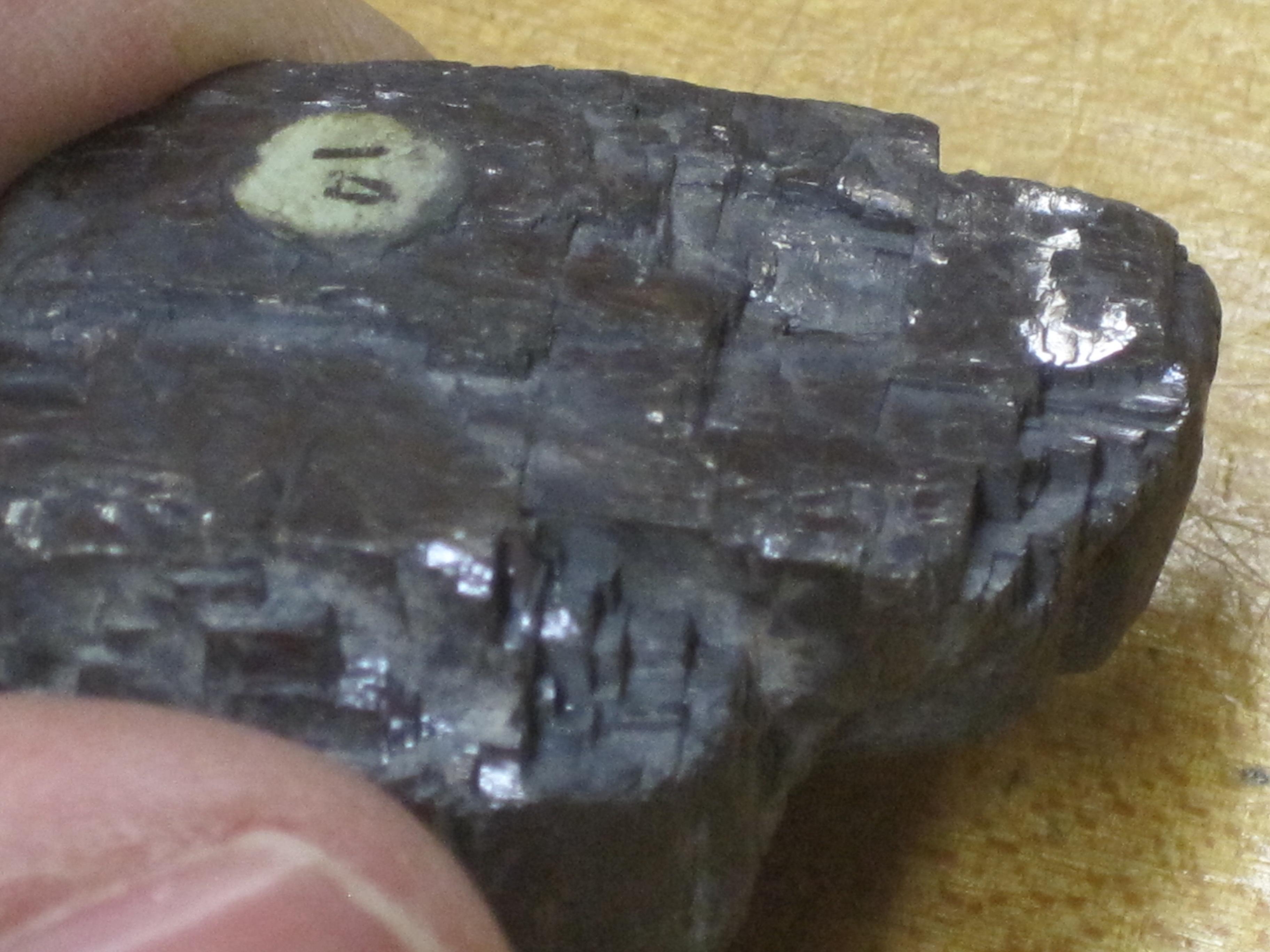
Fracture: the broken surfaces are not smooth planes; breakage is irregular.
 Examples: rough, ragged, uneven
Examples: rough, ragged, uneven
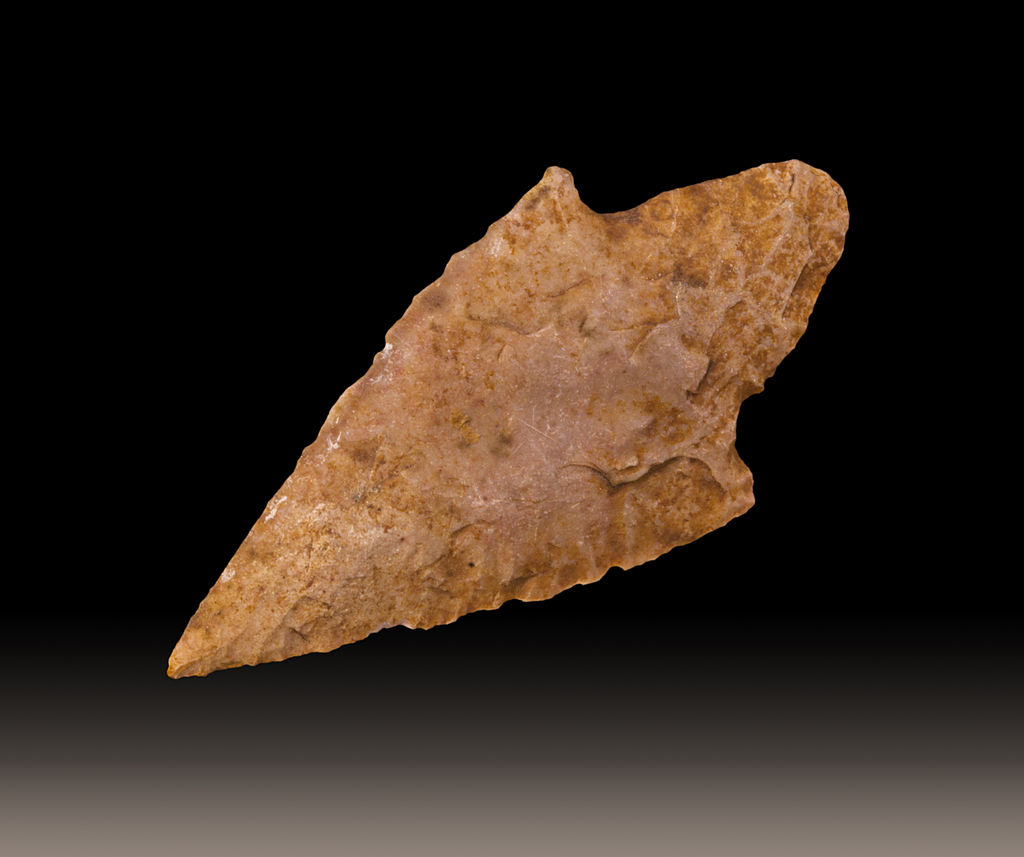 Conchoidal
Conchoidal
-
-
Specific gravity
The ratio of the weight of a mineral to the weight of an equal volume of water.
Specific gravity tells you how many times as heave as water the mineral is
Specific Gravity = (weight in air) / (loss of weight in water)
-
Color
The outward color, NOT streak color
Color is usually not an important quality
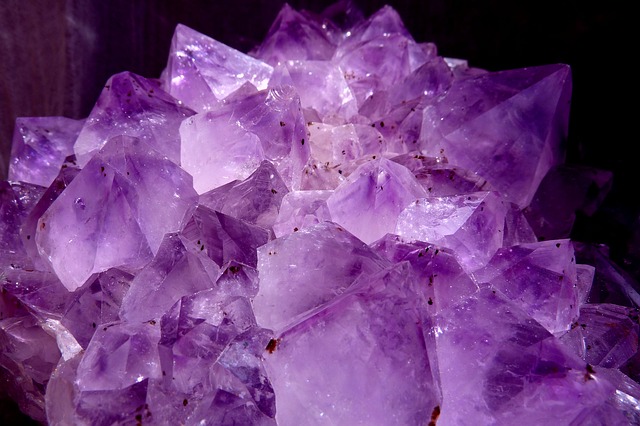
Some minerals vary in color; e.g. quartz can be: clear, white, pink, purple, smokey.
Many minerals have the same colors or similar colors; e.g. fluorite and quartz can both be purple.


-
Special characteristics
-
Taste
 Halite (table salt)
Halite (table salt) -
ShapeRecangular, cubic, pyramidal, etc
-
Double refraction

- Fluorescence
- Radioactive
-
-
Transparency
The ease with which light will pass through it.
- Transparent: most light passes through
- Translucent: some light passes through
- Opaque: all the light is absorbed or reflected
